Heat Exchanger Function And Features
About heat exchanger
1.Fin type

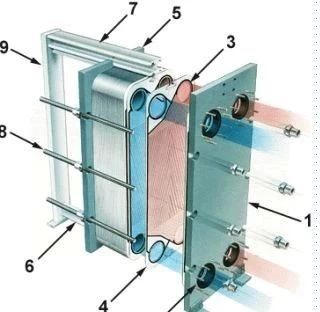
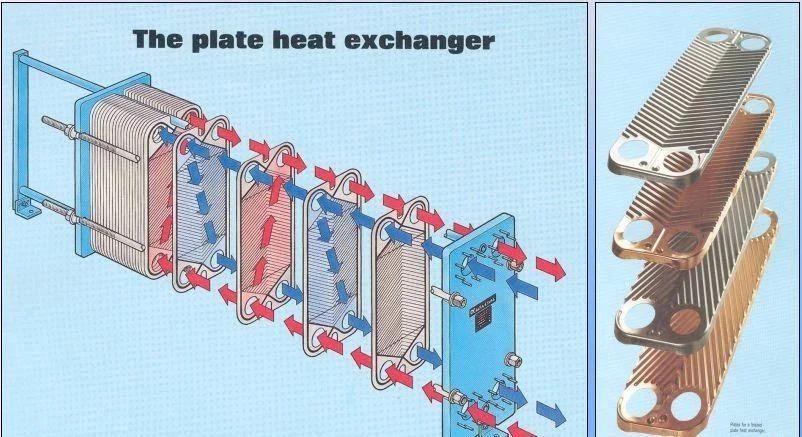
2.Plate-type
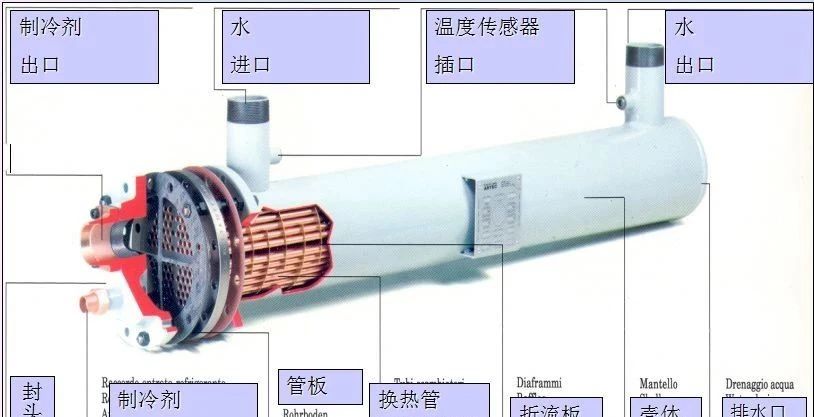
3.Shell-and-tube
Heat exchanger system
1.Air cooling/cold air system
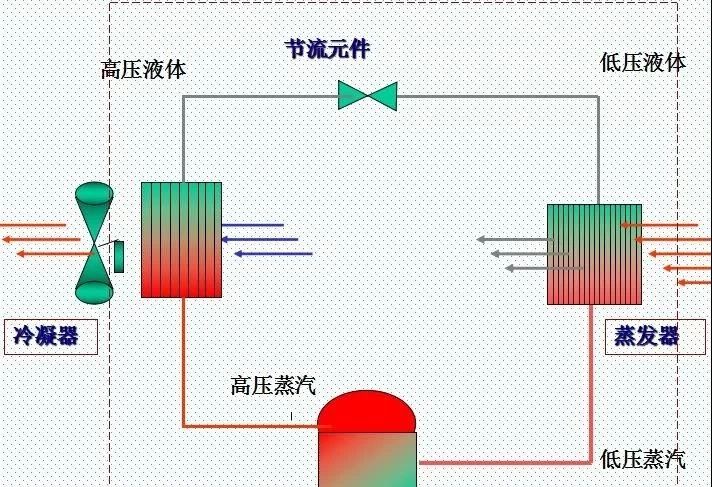
2.Air cooling / cold water system
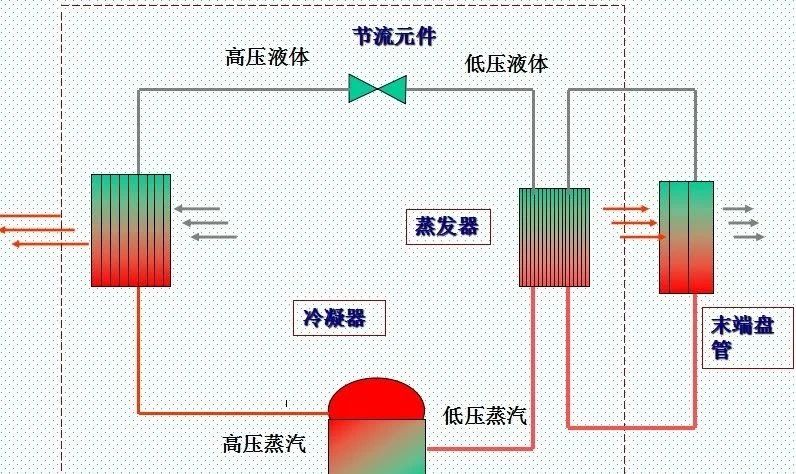
3.Water cooling/cold air system
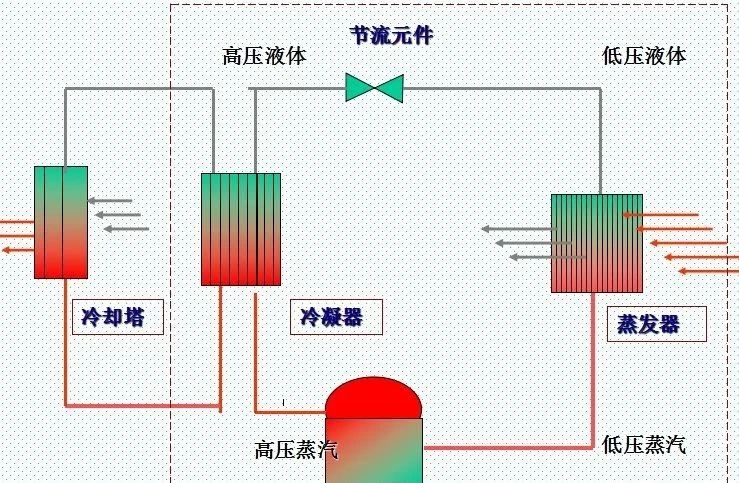
Condenser structure and characteristics
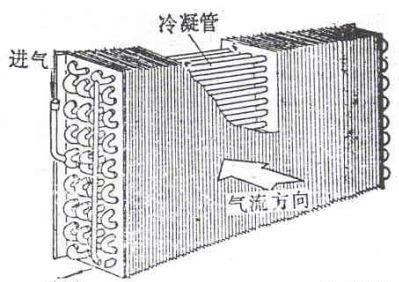
1.Air-cooled
Air is often countercurrent, which is less efficient than water-cooled condensers, and is used in small and medium-sized generators.
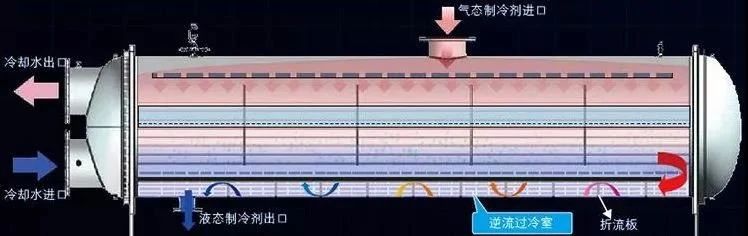
2.Horizontal shell - tube condenser
There is a partition in the end cover to divide the heat exchange tube into several processes, and most of the even-numbered processes are used to make the pipes on the same side. The refrigerant travels through the shell side,R22 condenses outside the tube, enters the air in the upper part, and discharges from the lower part. The cooling water runs through the pipe; the bottom goes in and the top goes out. Water and R22 flow in the opposite direction. The heat transfer coefficient is higher (compared with air cooling), the cooling water consumption is low (compared with the vertical type), and it is widely used.
3.Plate-type condenser
The plates are stamped and formed by stainless steel sheets. The refrigerant and cooling water flow between the sheets, with sufficient contact and high heat exchange efficiency. The plate heat exchanger only needs 1/2 to 1/4 of the area of the shell-and-tube heat exchanger to achieve the same heat exchange effect, but with less resistance loss, small footprint, complicated manufacturing process, high price, and easy blockage.